The benefits of mRNA COVID-19 vaccines outweigh the small risk that they may cause heart inflammation, as the jabs reduce hospitalisations and deaths, an advisory panel of the World Health Organisation said.
In a statement, the WHO said that reports of two rare conditions - myocarditis, an inflammation of the heart, and of its lining, called pericarditis - had typically occurred within days of vaccination, mainly among younger males after the second dose.
"Very rare cases of myocarditis and pericarditis have been observed following vaccination with the mRNA COVID-19 vaccines," it said, referring to the two vaccines using such technology, by Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna.
"The benefits of mRNA COVID-19 vaccines outweigh the risks in reducing hospitalisations and deaths due to COVID-19 infections," it said.
Available data suggested myocarditis and pericarditis following vaccination was "generally mild" and responded to treatment such as rest or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, the WHO said. "Follow-up is ongoing to determine long-term outcomes," it said.
"Vaccinated individuals should be instructed to seek immediate medical attention if they develop symptoms indicative of myocarditis or pericarditis such as new onset and persisting chest pain, shortness of breath, or palpitations following vaccination," it added.
Earlier on Friday, Europe's drug regulator said it had found a possible link between very rare heart inflammation and COVID-19 vaccines from Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna. It too stressed that the benefits of the shots outweighed any risks.
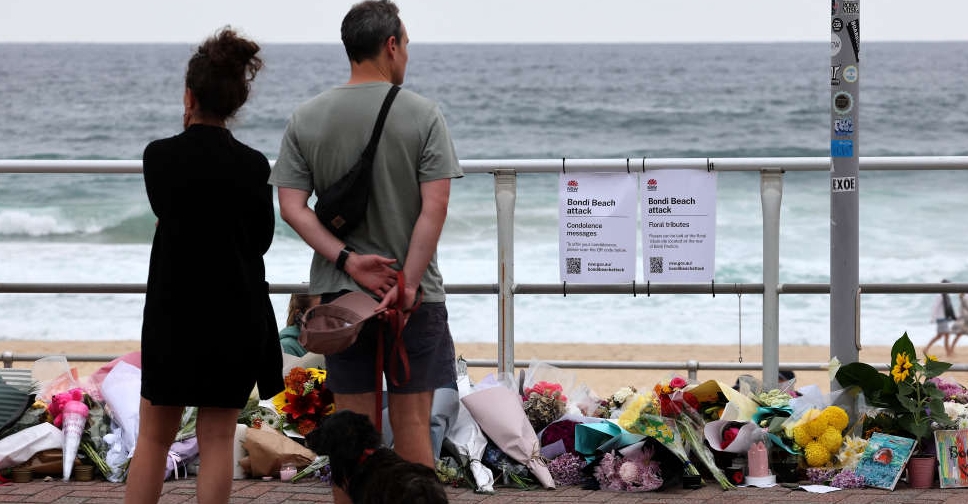



 Philippines confirms visit by alleged Bondi gunmen amid terrorism concerns
Philippines confirms visit by alleged Bondi gunmen amid terrorism concerns
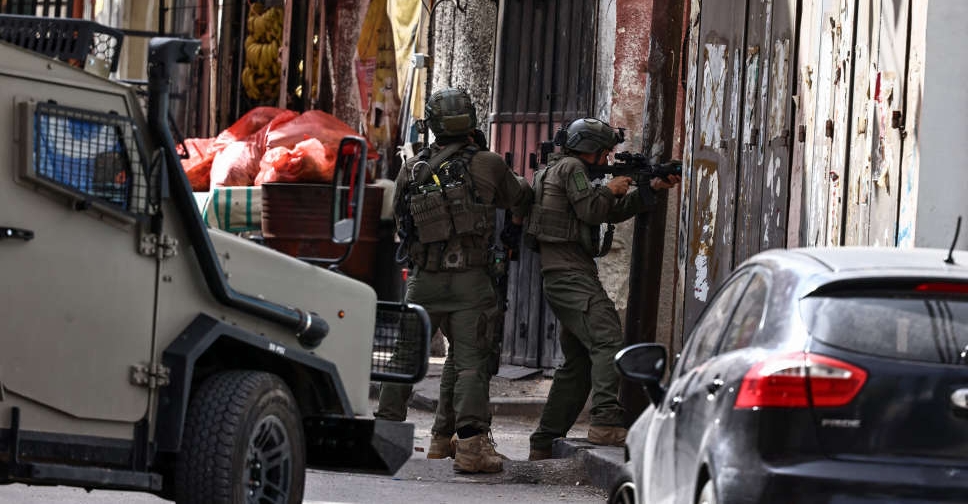 Israeli forces kill Palestinian teen in West Bank, health ministry says
Israeli forces kill Palestinian teen in West Bank, health ministry says
 Trump sues BBC for defamation, seeks up to $10 billion in damages
Trump sues BBC for defamation, seeks up to $10 billion in damages
 FBI foils 'terror plot' targeting Los Angeles
FBI foils 'terror plot' targeting Los Angeles
 Hong Kong court finds tycoon Jimmy Lai guilty in landmark security trial
Hong Kong court finds tycoon Jimmy Lai guilty in landmark security trial




